Organizing is one of the four important activities of a manager. However, what is the organizing function of a manager? Also, why is it important? Here we shall try to understand what is organizing in management and how to use it to improve managerial skills.
Contents
POLC framework
There are different types of managers, working in various departments and positions. Nevertheless, we can simplify the role of management in an organization. Consequently, we may understand the functions of a manager is through the POLC framework. This framework suggests that the roles of a manager can be described in four types of work: Planning, Organizing, Leading, and Controlling. In this article, we focus on the organizing work of the manager.
What is Organizing in management?
Organizing is the process of managing different resources to create value for the firm. Typically, managers bring together resources like finance, human resources, technology together to produce an output for the customers. This output could be a product or a service. In a more practical sense, we can also say that organizing is coordinating different teams, bringing people together, and empowering them with respective roles. All of this is done while keeping in mind the larger end goal. The subordinates typically focus on their tasks while the manager organizes these tasks to create the desired end results or objectives for the firm.
Therefore, we can say that there are some key aspects of organizing:
- Co-ordinating with people
- Motivating them for the work
- Distribution of work
- Synchronizing the work
Six facets of organizing
Organizing can also be visualized in the form of six aspects as represented in the diagram below:
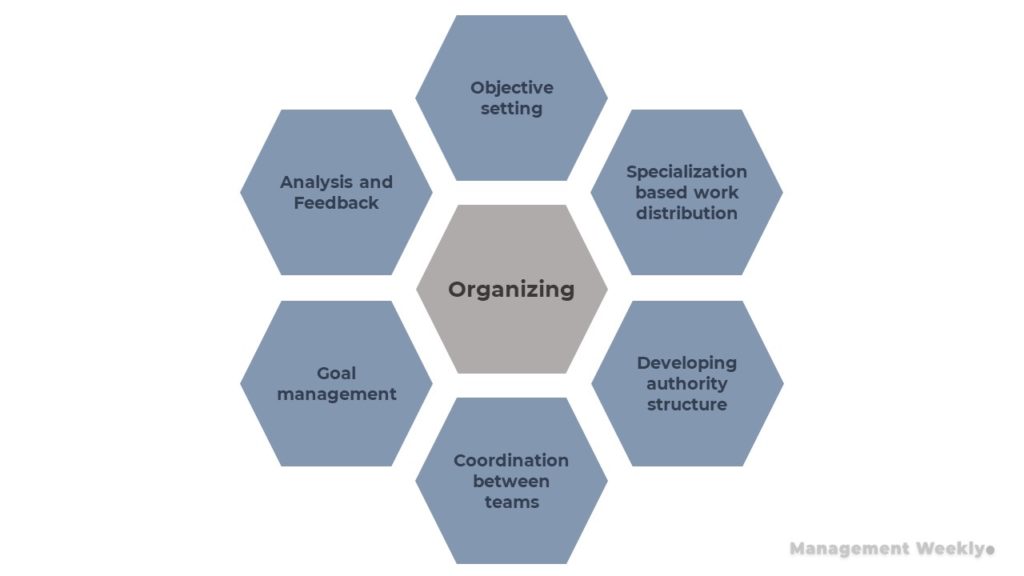
Firstly, and most importantly, we should set our objectives. Objectives are statements that define the goals for the organizational activities. It could be to launch a new product in the market or it could be to act upon supply chain disruption. Once the objectives are set, we can proceed to develop the project management plan. This requires us to prepare the list of inter-dependent activities that are required to meet the objectives. Managers are expected to identify the set of activities that are required for the required objective.
Specialization based work distribution
Secondly, we need to assess, the type of work required. This will help us divide the work between the workforce. We can use the concept called ‘specialization of labor.’ Although, you may be aware of the basic concept, here is a quick recap. Specialization of labor looks at dividing the work so that individuals only work on a specific type of task. This type of work is called specialization of labor. The concept comes from the days of the pin factory. The father of scientific management, Adam Smith envisioned increased productivity if each worker did a specific type of work like only bending the pin. The second worker made the second bend, and so one. This was in contrast to the traditional system where each worker took the blank pin and made all the bends to create the pin.
However, keep in mind that modern work distribution is very different. The pin-factory type specialization makes the workers get bored due to repetitive work. It causes fatigue and burnout. When we talk about specialization-based work, we mean work distribution based on the area of expertise. Modern management principles recommend that people bring in learning and expertise together and help each other out with ideas.
Developing authority structure
Once the work has been clustered based on the different areas of expertise, the work needs to be delegated. Delegation involves the transfer of authority for a particular task. The concerned managers are handed specific goals. Additionally, the managers are also given authority for the tasks. Authority is given in the form of different levels. These levels form the authority structure. We require authority structure to facilitate smoother workflow. It helps in increasing the efficiency and timely completion of the goals. You may follow these golden rules of goals to help you in fulfilling them.
| Management Level | Authority overview | Example |
| Top management | Developing strategy, policies and protocols | Foreman, Team Leader |
| Middle management | Managing the departmental goals | Area Sales Manager, Operations Manager |
| Lower Management | Monitoring and supervising the workers directly | CXOs, Directors |
The table above summarizes the authority structure in an organization. Typically, we classify the authority in three tiers of management levels: top management, middle management and lower management. Further, we should note that authority is closely tied to responsibility. The higher the authority, the higher is the responsibility. Responsibility makes the managers accountable towards the completion of their goals.
Coordination between teams
Once we have the authority structure in place, we look into the relationship between and within teams. Firstly, coordination enables channels of communication between teams. Communication is key to align the entire firm along with an objective. It also helps in assessing the progress of work. Secondly, coordination also helps in developing channels of feedback.
As a top-level manager, it is essential to coordinate between different departments. It is an innate tendency to have a myopic perspective. Mid-managers may be focused too narrowly on the fulfillment of departmental goals. At times, this perspective may conflict with the goals of other departments or the organizational goals. This coordination work is an essential part of what is organizing in management, especially top management. The manager’s role also requires them to be visionaries for the organization.
Goal management
Goal setting is only the first step towards fulfilling the organizational objectives. We need to monitor the progress closely. This helps in prognosis of problems and also helps in fixing them in time. Here are some key aspects of goal management:
- Problem definition
- Specification of goals
- Goal setting
- Progress tracking
- Monitoring and guidance to lower levels
- Feedback and Reporting to higher levels
The first step in goal management is defining the problem. In the case of mid-managers and lower managers, the problems are given by the higher level in the form of problem specification. This helps in defining the problem. Once the problems are defined, managers have to set goals. One of the well-known approaches is to set SMART goals. Further, the progress has to be tracked. The managers have the responsibility to guide their subordinates. On the other hand, they are also expected to report to their superiors. This is where the authority structure we had established earlier, comes into play. Another way to look at goal management is to look at it from people’s perspectives. Goal management is essentially managing people at upper and lower levels.
Analysis and Feedback
We cannot discuss contemporary management without referring to analytics. Analytics is the use of information to improve performance. We may use statistical tools to understand how we are performing with respect to key performance indicators or KPIs.
Further based upon the analysis, managers are expected to provide feedback. This feedback helps in correcting any problems with the approach. Sometimes, work may need to be expedited to meet downstream dependency. All of these decisions have to be taken once the required information is available.
Some Frequently Asked Questions about organizing:
Organizing is the kep to organizational success. It helps in excuting strategies to fulfil organizational goals. It also helps in boosting the performance and work satisfaction of employees.
1. It helps in structuring the work
2. Increases the work efficiency
3. Improves the job performance for employees
4. Reduces the wastages
5. It helps in managing any contingencies
No, planning is an essential part of organizing. If we skip planning stage, there may be problems in the later stages like organizing, leading and controlling.
Planning is the precursor to organizing as per the POLC framework. Planning forms the first step towards meeting the organizational goals. Planning helps us take the stock of the requirements and formulate these goals. It also helps us in developing work execution plans to fulfil these goals.
Both of these are correct. However, the usage depends on the type of English followed in your organization. American English usage is ‘organization.’ On the other hand, we use ‘organising’ for British English. Also, ensure that you use one form consistently across a document.
Mobilizing is related to deployment of resources. On the other hand, organizing is about the holistic approach towards fulfilment of organizational goals.
