As a researcher or analyst, one needs clarity regarding the pros and cons of a sampling method. Therefore, systematic sampling advantages and disadvantages will help you choose this sampling method for your study/analysis. Here we shall look at the various aspects of systematic sampling. Additionally, we shall try to understand it from different perspectives.
Contents
An introduction to Systematic sampling
Definition of Systematic sampling
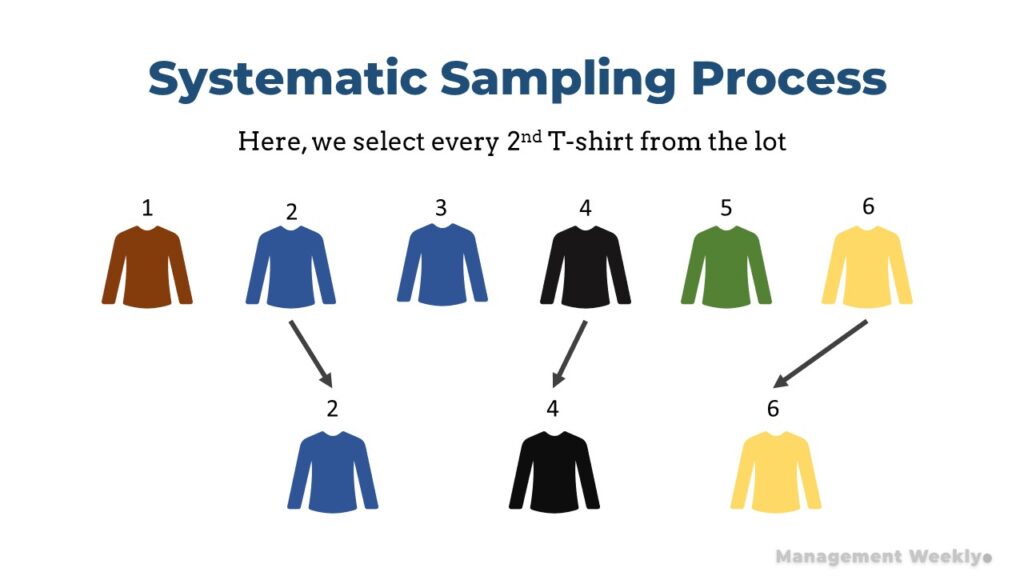
Systematic sampling is a common data gathering procedure. In this type of sampling, we collect the elements from a population-based upon a probabilistic collection method. In plain English, this means that we select the elements spaced out at some fixed interval. For example, please see the illustration given below. Here we select every 2nd T-shirt from the lot. This is an example of systematic sampling. We could have even chosen every 3rd T-shirt from the lot and so on.
Characteristics of Systematic Sampling
Systematic sampling is easier to understand and implement. It also makes the data collection more robust compared to convenient sampling. However, it differs slightly from simple random sampling. In simple random sampling, all the samples have got an equal probability of being selected. However, in systematic sampling, we do not have that. In systematic sampling, only each of the elements has an equal probability of getting selected.
It can also be understood in terms of a three-step process. In the first step, we calculate the total population. In the second step, we asserted the sample size that is required for the study. Then we divide this population by the sample size. Therefore, we get the interval for collecting data. In the third step, we start collecting data from the nth individual in the population. This is the same end that we had calculated in the previous step.
Where do we use systematic sampling?
When the data is of higher quality and it is reliable, then we may go for systematic sampling. Therefore, we should avoid systematic sampling in situations where data could be manipulated. This will lead to erroneous results and also it will give misleading data visualization at the end of the analysis.
We use systematic sampling in research to avoid any kind of data selection biases. For instance, data that has been collected using a probabilistic method, like systematic sampling, lead to a higher quality of raw data.
What is an example of systematic sampling?
Let us consider the monthly output data of a small garment factory. We may be interested in the total units of a product made in different months. Now, let us say, we want to do a systematic sampling of the production. Consequently, we select monthly data for every third month (Sample 1 as shown in the table below). This would be an example of systematic sampling. On the other hand, we could also collect data for every six months (Sample 2 as shown below). Even that would be an example of systematic sampling. However, if you randomly select months 1,3,4, and eight (Sample 3). Then it is not a systematic sampling.
| Month | Monthly output | Sample 1 | Sample 2 | Sample 3 |
| January | 1200 | 1200 | 1200 | 1200 |
| February | 1250 | |||
| March | 1300 | 1300 | ||
| April | 1150 | 1150 | 1150 | |
| May | 1000 | |||
| June | 800 | 800 | ||
| July | 1200 | 1200 | ||
| August | 1250 | 1250 | ||
| September | 1300 | |||
| October | 1300 | 1300 | ||
| November | 1250 | |||
| December | 1350 | 1350 |
Systematic sampling advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages
- The first advantage of using a systematic sampling is that this type of data gathering procedure is fairly simple.
- At times, data collection is done manually by the researcher. In that case, it makes sense to have a systematic sampling as it eases the data collection process.
- It eliminates the biases of data collection present in a non-systematic method.
- It has a lower risk factor as well.
- This method is also useful to create a good distribution of the members of a population.
Disadvantages
- One of the biggest downsides of systematic sampling is the poor quality of sample if the population has periodicity (Iachan, 1982)
- Therefore, in a population that does not have randomly occurring data, it cannot be administered.
- It also introduces some risks of manipulation by researcher.
- Another disadvantage of this method is that we based our assumption on a determinate (measurable) population size. In a lot of situations, we may not know the size of population or it may not be determinate.
- In the pecking order of the sampling techniques, it is not the best one. Simple random sampling is better than systematic sampling. Also, stratified random sampling is better than simple random sampling.
What is systematic judgmental sampling?
Systematic judgmental sampling is yet another method. It combines the techniques of systematic sampling as well as that of judgement sampling. However, this type of sampling should be avoided. It introduces the errors from both these types of samplings. Therefore, we should avoid it.
