An organization needs a set of suppliers and distributors to function properly. A supplier chain network is this interconnection between these entities. These entities help the organization in procuring raw materials. They also help in distributing the products. A McKinsey report says that an efficient supply chain network can reduce the working capital requirement by up to 25% and increase the EBIT by up to 4%.
Contents
Why do we need a supplier chain network?
A Supplier Chain Network (or Supply Chain Network) helps the managers to design and optimize the movement of resources. There are two important factors to consider. The first is the reduction of the time. The second factor is the reduction of the costs. The entire supply chain network can be modeled mathematically. Subsequently, it can be optimized. This helps in designing a supply chain network that is fast, resilient, and efficient.
A supplier chain network can help increase EBIT by up to 4% and reducing working capital by 25%
Apart from the traditional requirements of time and cost, there are two additional requirements. These two requirements are relatively new in terms of supply chain management. However, they are becoming more and more important.
- Risk mitigation.
- Sustainability.
Nevertheless, the key takeaway from this is that supply chain network modeling is a very involving process. Also, it has huge implications for the firm’s profitability. Automation of processes also helps in reducing the risk and managing uncertainty.
An example of a supply chain network.
One of the best examples of a supply chain network is that of Intel. We shall trace the steps from the basic silicon crystal to a CPU as discussed by Sheffi in the book Resilient Enterprise. The first step in manufacturing starts with a Silicon crystal. Their first supplier is Toshiba Corp, Japan. They take a Silicon crystal and develop it into ingots and finally into silicon wafers. The Silicon wafers are about 30 centimeters in size. These wafers then reach Intel’s fabrication centers in the US. The actual chip manufacturing process takes place in these centers. They etch circuits into these chips. Subsequently, they forward it to Malaysia. This lab does the final assembly. They also do a quality check. They send it back to the US for distribution.
This process may seem a little bit convoluted or confusing. However, it is important to maintain quality as well as to increase reliability. Each center that specializes in a particular task will churn out a much higher quality product than one center that does all the jobs. Other companies also use a similar model. A larger number of companies are embracing a global and diverse supply chain network.
Internal factors
Some of the key internal factors that affect the design and optimization of supplier chain network are:
- Key targets for supply chain KPIs
- Requirements from other functional areas of an organization.
- Resources available for transportation, storage, etc.
- Time constraints
External factors
An organization has constant interaction with the external environment. These factors are mostly macroenvironmental factors. They play a major role in shaping the supplier chain network.
- Regulatory benefits or restrictions
- Tax requirements
- Deferred tax liability
- Labor cost
- Subsidies, fines and surcharges
These factors impact the cost of logistics. Therefore, they are factored in the model of supply chain network.
Common issue in analysis of SCN
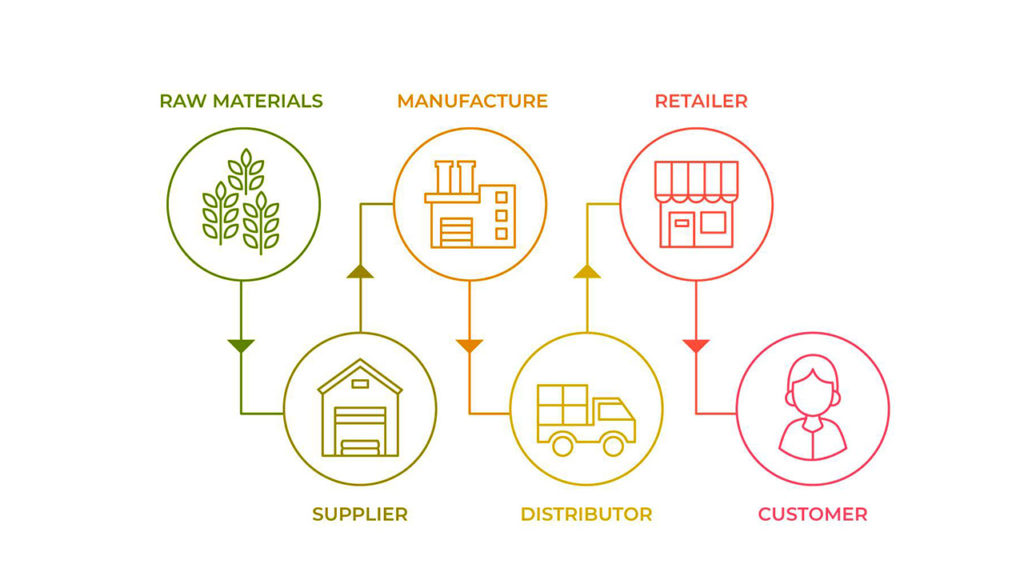
One of the most common mistakes is to neglect the distribution part of the supply chain. It is far too common to focus only on the supplier side and neglect the distributor side of the supply chain network.
Firstly, the distribution system has physical equipment. Their performance degrades over time. This can reduce the performance and increase the cost.
Secondly, the distribution systems also need to be modelled for their capacity. The distribution systems work most efficiently under certain range of workflow. This flexibility can be enhanced by having a distribution partner that allows for scaling of operations.
Thirdly, we should factor in the demand forecasting for the supplier chain network on the distribution side. Scheduling and forecasting help in even out any unforeseen changes in the volume.