One of the critical factors for the going concern of a firm is to satisfy the customers. Dissatisfied customers are the first step towards the ruin of any business. Kano model can be a useful tool to understand what product features makes your customers happy. It can, therefore, help us unlock customer happiness through delightful products. We shall discuss the Kano Model example with easy to understand explanation. Subsequently, we shall take it a step further with the ready to use survey.
Contents
Noriaki Kano
Professor Noriaki Kano is an educator from the Tokyo University of Science, Japan. He was curious about understanding customer satisfaction. In the late 1970s It was believed that to make customers satisfied, you needed to improve all the features of a product. This belief was so widespread that companies put in an exorbitant effort in improving all the attributes of products. This was a waste of their resources. Additionally, it did not work as well as it was intended. When you try to do everything better, you end up making everything worse. You have to prioritize. It is also important to understand that some attributes may have a negative impact on satisfaction. Sometimes, satisfaction may decrease if an attribute increases.
In simplest of terms, the Kano model helps you understand the attributes or features that your customers cherish. You can then prioritize your efforts to excel in these features and rule the market.
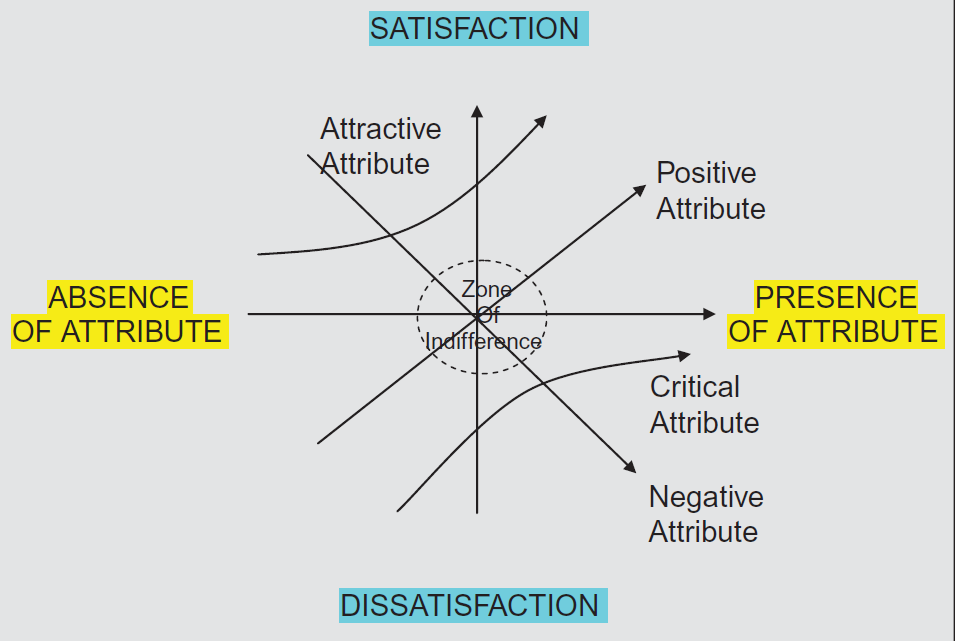
The Kano Model
There is a total of 5 different levels of importance of a feature. We shall use some standard names here, as per the Kano model:
- Reverse
- Indifferent
- Attractive
- Performance
- Must-be
Reverse attributes
The worst type of feature you can have in your product is one which is disliked by your users. You must have seen some of the cheap electronics with very bright LEDs on them. A lot of people would dislike them. It makes more sense to remove those features than to retrain them. Your consumers will have lower satisfaction from using your products because of these reverse features. In terms of service industry, this can also be thought of as some useless times consuming steps in the process.
Indifferent attributes
These are those attributes that make no difference to the satisfaction. Sometimes products are stuffed with features that people don’t use. These kind of features are attributes mean nothing to people. They will not change the satisfaction at all. Therefore, it makes sense to remove these features. When we try to mathematically model in different features, we come up with a very low covariance with satisfaction.
Attractive attributes or Delighters
As the name suggests, these attributes are those that can surprise the customers positively. They may not be expecting these attributes. However, when they find out these attributes, it would lead to a higher satisfaction. Do you remember the snake game on Nokia phones? Those are the kind of delighters. We never bought a phone for playing a particular game back then, but then when they were included they added value to our overall experience.
Performance attributes
These attributes have a direct relationship with the satisfaction in the products. One of the simplest examples would be the processing speed of a computer. As the processing speed increases, we get more benefit from a computer. Therefore, we can say that it is a performance attribute. These kind of attributes are also called one dimensional attribute. This is because their covariance with the satisfaction from the product is almost close to 1.
Must be attributes
As the name suggests, these attributes are indispensable. We would not even buy the products if these were not there. In other words, we can say that absence of these attributes increased our dissatisfaction with the product. These also set a threshold or cut off for the features. They will look how these affect are satisfaction. However. Overall they have a curvilinear relationship with the satisfaction. This means that their presence is necessary. However, if these attributes increase, they may not increase the satisfaction.
Questionable attributes (discontinued in current Kano models)
Questionable attributes were included in the original Kano model. One way to visualize these attributes would be to think of a confusing feature. These features may not have consistent response from people. These kind of attributes do not fall into the five type of attributes that we have discussed earlier. One of the examples would be cars spoilers. Car spoilers are attachments to the bodies, especially the rear part of the car. They have some aerodynamic advantage at higher speeds. However, some of the people may not like them, especially when they add more cost to the car.
The updated Kano Model
Now we shall look at the updated Kano Model. There have been some changes applied to the original Kano Model over the years. Here we’re going to look at one of the modified Kano models that were developed for the tourism industry. It was made by Amy Gregory in 2011.
The Kano survey questionnaire
Now let us look at the Kano survey questionnaire. This would help you to prepare a survey for measuring the important attributes. For each of the attributes, we need to assert and the functional, as well as the dysfunctional response. In other words, If you had a certain feature, how would you feel? Similarly, how would you feel if you did not have a certain feature? Originally pronounced suggested using a 7 point scale. However, administering a 5 point scale is easier. We shall have the five different ranges of responses from “like” to “dislike.” We shall consider the Kano Model example of a smartphone. For simplicity, we are considering only a subset of all the attributes. However, the process shall be the same for other products and for more number of attributes.
The Kano Model example of a smartphone
| Attribute | Question Type | Questions |
|---|---|---|
| MicroSD Card slot | Functional | How would you feel if the smartphone had an Micro SD Card slot ? |
| How would you feel if there expandable storage in the phone? | ||
| Dysfunctional | How would you feel if the product did not have Micro Sd card slot? | |
| How would you feel if there was less storage in the phone? | ||
| Zoom camera | Functional | How would you feel if the smartphone had a zoom cameras? |
| How would you feel if there were more range of cameras in the phone? | ||
| Dysfunctional | How would you feel if the product did not have a zoom camera? | |
| How would you feel if there were only one camera in the phone? | ||
| Free back cover | Functional | How would you feel if the smartphone came with a free back cover ? |
| How would you feel if there were free accessories with the phone? | ||
| Dysfunctional | How would you feel if the product did not have an included back cover? | |
| How would you feel if there was less accessories with the phone? | ||
| Headphone jack | Functional | How would you feel if the smartphone had a headphone jack? |
| How would you feel if you could listen to any headphone/earphone with your phone directly? | ||
| Dysfunctional | How would you feel if the product did not a headphone jack? | |
| How would you feel if there was no option to connect regular headphones/earphones directly with your smartphone? | ||
| Stereo speakers | Functional | How would you feel if the smartphone had stereo speakers? |
| How would you feel if there were more than one speaker in the phone? | ||
| Dysfunctional | How would you feel if the product did not have stereo speakers? | |
| How would you feel if there was only one speaker in the phone? |
All of these responses are collected on five point basis. The different points in this scale are:
- Dislike
- Tolerable
- Neutral
- Expected
- Like
Once we have these responses, we can process them. However, we need to convert these simple five-point responses into the categories of attributes we had discussed earlier. Let us take an average of both the questions under functional type and round them. Similarly, we do it for Dysfunctional and round them, call the average value of functional as ‘F’ and average value of Dysfunctional as ‘D.’ In order to do this, we shall use the key that provided below:
| F | D | Interpretation |
| 1 | 4 | Reverse |
| 3 | 3 | Indifferent |
| 5 | 3 | Attractive |
| 5 | 1 | Performance |
| 4 | 1 | Must-be |
Once you have figured it out for all the attributes, you can take your call on what to prioritize. The ‘Must-be’ attributes should take up most of your attention, then the ‘performance’ attributes. We also need to look into how these attributes fit into our product/market fit which we can do through the Ansoff Matrix. As an assignment, you can develop and collect questions for our Kano model example of the smartphone.
