Michael Porter has given us some of the most powerful tools in strategy. One of his most popular contributions was Porter’s Generic Competitive Strategies. What are these generic strategies? Why are they important? How to use these generic strategies?
Contents
Introduction to the generic strategies
It is quite interesting to know how the porter’s generic competitive strategies were developed. Until 1980 it was observed that the impact of marketing was not uniform for different companies. Some companies were able to extract more returns from marketing efforts than others. While a more obvious solution was important in the marketing mix, there could be other factors that contributed to this.
Michael Porter started looking at the profitability of the companies. He realized that there was a pattern. There are two kinds of companies which for more profitable. Firstly those companies which have a higher market share. Secondly, those companies which have a much smaller market share. He noted that companies that are somewhere in the middle with moderate market share did not perform as well.
The solution
He opined that this could be explained in the strategy that the firms pursued. He proposed that the larger firms played the cost game. Also, the smaller forms targeted a particularly profitable segment.
Using this justification he developed three kinds of generic strategies that firms follow. These strategies came to be known as Porter’s generic strategies. He published his ideas in a book titled ‘ Competitive Strategy ‘ in 1980.
How to make sense of Porter’s generic strategies?
Firstly, let us look at the building blocks of Porter’s generic strategies.
Market segments
First let’s look at market segments. Market segments are smaller sub groups of your target market based on certain characteristics. Customers from the same market segment are expected to behave in a similar manner.
Competitive Advantage
Secondly, let us look at competitive advantage. competitive advantage is the benefit that a firm gets due to a particular position in the market. For example, let us say that you you are a car manufacturer. You you make cars that are highly fuel efficient. In this case fuel efficiency could be your competitive advantage.
Differentiation
Now let’s look at differentiation. Again, taking the cards example. let us consider that there are 10 different manufacturers in the market. However, all these cars are more or less alike. Then a new player enters the market. The new car manufacturer makes cars that can run on electricity. This differentiates the manufacturer from the rest of them. Similarly thanks like brand, quality or features could be differentiating factors.
Scope of Focus
Next let us look at the scope of focus. A firm may opt for a narrower focus. In other words it characters only to particular segment. For example a car manufacturer that specialises in making SUV. On the other hand another manufacturer that makes different kinds of cars like sedans, hatchbacks and SUVs has a broader approach.
Cost Advantage
Finally let us define what is cost advantage. Let us see that there are two different. Both of these products are quite similar. However, one of them is slightly cheaper than the other. In this case the cheaper product will be sold more easily. Therefore we can say that the sperm has got a cost advantage.
Porter’s generic strategies
According to Prof. Michael Porter, the firm’s position could be categorized into one of the two broad strategies. A firm could either use cost advantage or differentiation. Meanwhile, the firm could have a broader scope or narrow scope.
Thereby a firm can have either of the three strategies:
- Cost leadership
- Differentiation
- Focus
Now let’s create Porter’s generic strategies matrix. This will help us visualize the generic strategies better.
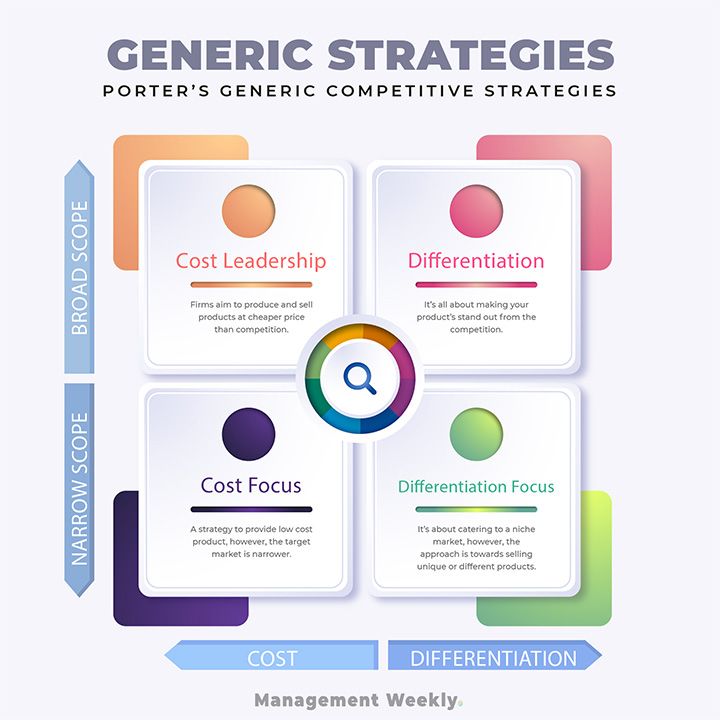
The Cost Leadership Strategy
We have already discussed the importance of cost advantage. This advantage translates into cost leadership for the firms.
For instance, firms that can produce and sell products at a cheaper price compared to the competition will have higher sales. this also means that the firm can utilize economies of scale to bring the costs down. this helps the form reduce the cost of goods sold. On the other hand higher sales means that the revenues are higher. Thereby tapping into the virtuous cycle of profitability.

How to become a cost leader?
A firm can attempt to become a cost leader by employing the cost leadership strategy. It is easier said than done. However there are certain ways to establish yourself as the cost leader in the market.
Firstly, cost leaders are generally larger firms. Larger firms have better access to capital. They also have bigger assets. This helps in the economies of scale.
Secondly, cost leaders also has access to better human resources. They have access to better managers designers and professionals. Organisations that are caused leaders should have technical prowess to make the products at a cheaper cost.
Thirdly, being a cost leader also depends on how you can leverage the different aspects of the firm. Then it’s to be a Synergy between the different departments, the supply chain and the distribution channels.
The Differentiation Strategy

Differentiation is all about making your products as unique as possible. When we talk of uniqueness it is not making a product that is different from others. The products also need to be attractive. The unique features should be desirable.
Let us see that some car buyers value safety. This particular feature can become the point of differentiation for a manufacturer. Volvo positions itself as the maker of safer cars.
However, there are certain industries where it is very difficult to sell products just based on a single feature. For instance the smartphone industry. The smartphone manufacturers have to cater to a wider variety of customer needs. they cannot sell product based upon a single feature alone.
How to develop the differentiation strategy?
It is easier for firms to position themselves as a differentiation player. It is also easier to make products and sell products that are differentiated. generally these products have higher loyalty from the buyers. now let us look at some of the ways in which a firm can use differentiation strategy.
Firstly, the firm needs to find a particular market requirement. A segment of market with specific requirements. This is required for providing differentiated products. This can be done through research. Firms can do customer journey mapping or Market surveys to find out specific requirements.
Secondly, in order to become a differentiation leader the firm should have strong base in research and development. The form should ideally possess intellectual property to counteract the competition.
Thirdly, the firm must also have an image that is congruent with its offering. For example, the safety of Volvo cars has been established through various crash tests across the world. Any new firm that wants to position itself in this niche, has to pass the rigorous crash tests with equivalent or better scores than Volvo.
The Focus Strategies
A focus strategy essentially means that the firm attempts to target only a narrow segment of the market. Within this segment, it could either try to have a cost advantage or a differentiation.
A focused market player enjoys one of the highest loyalty is from the customer.
There are some disadvantages if you look at the focus strategy. Let’s consider the porter’s five forces for the focus strategy. These firms will have a hard time negotiating with the vendors due to the lower volume. It would thereby increase the bargaining power of the suppliers. These firms are also highly vulnerable to broadly scoped firms.
There are two types of focused strategies:
- Cost Focus
- Differentiation Focus
Cost Focus
Cost Focus is one where the firm wants to sell products that have a lower cost compared to the competition, albeit to a narrower market. Also, this is a type of Porter’s generic competitive strategies.
There are some small differences between Cost Leadership and Cost Focus. Firstly, the company attempts to provide a low-cost product only for a particular customer segment. Let us take the example of OnePlus. The unique selling proposition of this brand of phone is that it provides flagship-level performance at mid-range prices. Secondly, the Cost Focus strategy also enhances customer targeting over the cost leadership strategy.
Differentiation Focus
Similar to the differences between Cost Leadership and Cost Focus, we see a parallel between the Differentiation and Differentiation Focus.
Firstly, in the Differentiation Focus, the firm attempts to target a particular market segment. Secondly, in this approach, firm attempts to sell the product based on its unique characteristics. For example, if we take the case of smartphone manufacturer Bellperre. It is a relatively unknown luxury smartphone brand from the Netherlands. They jazz up flagship phones like iPhones and Galaxies and sell them for prices in the range of $3000.
Stuck in the middle or the strategic hole
Porter proposed that these generic strategies need to be undertaken on their own. He proposed that a combination of these strategies will not yield good results for the firm. According to this reasoning if a product differentiates itself from others it should not be priced below them. This could signal lower quality to the customers. Thereby porter’s generic competitive strategies are incompatible with each other.
The combination of generic strategies was called stuck in the middle. one way to overcome this problem is to develop separate businesses that cater to different segments of the market.
Modern take on Porter’s generic competitive strategies
It has been around 40 years since Porter came out with generic strategies. Has it stood the test of time? Let’s find out.
Later studies have found out that companies need not strictly follow Porter’s strategies. The fact there are a lot of examples where companies have followed the ‘stuck in the middle strategy’ I am succeeded.
In fact, these companies were found out to be more successful than those which followed on one of Porter’s generic strategies. Some researchers have developed an alternative conceptualization for these strategies.
An explanation for this is that a low-cost strategy soon develops into a price war between the firms. It becomes very difficult for firms to provide the same value to the customers. Forms either race towards the bottom of the price or they start providing lower quality products.
An alternative to Porter’s Cost Leadership
There is a better way of looking at cost leadership. Cost leadership can be thought of in two ways. Low-cost strategy or Best cost strategy. In the low-cost strategy, the firm’s mindlessly reduces the price and try to provide a product at a low price as possible. On the other hand in the best cost strategy, the firms try to provide the best value at the lowest cost.
Customers are more interested in a value for money product rather than the cheapest product in the market. This is the reason why best cost strategy works better than cost leadership.
At the same time there have been other criticisms about Porter’s generic strategies. Porter’s strategies are quite vague. They also lack flexibility.
Important Questions related to Porter’s Generic Competitive Strategies
The combination of cost leadership and differentiation was considered non feasible by Michael porter. However modern researches and strategists consider a hybrid strategy as a better one.
Large firm’s which can have economies of scale can go for Cost Leadership strategy.